CATION EXCHANGE BUFFERS
CATION EXCHANGE BUFFERS
Recommended Buffers for Cation Exchange Chromatography*
To use the calculator, enter the buffer's concentration and temperature, then click on the corresponding button.
The following are the implicit rules of the calculator:
| The best buffers (white background)** | Less suitable buffers (light brown background)** | |
| Ionic strength at at pH=pKa | I ≈ 0.5 C | I ≈ 2 C |
| Concentration range | 1 - 500 mM | 1 - 130 mM |
| Temperature range | 3 - 37oC | 3 - 37oC |
| pKa0 (25 oC) | d(pKa)/dt ΔH0, kJ/mol |
Calculate pKa at given concentration and temperature |
Buffer name/dissociation type | Dissociation step | UV limit |
Notes |
| 1.92 | -0.0006 1.1 |
mM oC pKa |
Maleic acid H2L = H+ + HL-1 |
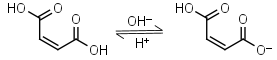 |
Opaque up to 270nm | Other pKa: 6.23. Can react with strong nucleophiles (e.g. thiols) by Michael addition. |
| 2.148 | +0.0047 -8.0 |
mM oC pKa |
Phosphoric acid H3L = H+ + H2L-1 |
H3PO4 = H+ + H2PO4-1 | Clear | Other pKa: 7.198, 12.35. Stabilizes many enzymes. Precipitates bivalent cations. |
| 3.128 | -0.0024 4.07 |
mM oC pKa |
Citric acid H3L = H+ + H2L-1 |
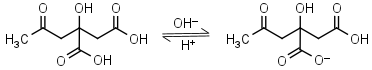 |
Clear | Other pKa: 4.761, 6.396. Binds to some proteins. Forms complexes with many metals. |
| 3.40 | mM 25oC pKa |
Malic acid H2L = H+ + HL-1 |
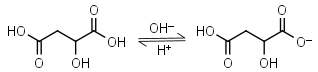 |
Clear | Other pKa: 5.11. Is chiral. Forms complexes with some metals. | |
| 3.75 | mM 25oC pKa |
Formic acid HL = H+ + L-1 |
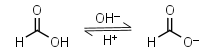 |
Clear | Slightly volatile, usually is sold containing 5-10% of water - difficult to dose in exact amounts. | |
| 3.86 | mM 25oC pKa |
Lactic acid HL = H+ + L-1 |
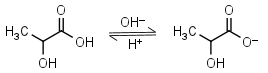 |
Clear | Is chiral. Usually is sold as ~85% solution in water - difficult to dose in exact amounts. | |
| 4.207 | -0.0018 3.0 |
mM oC pKa |
Succinic acid H2L = H+ + HL-1 |
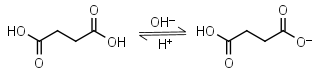 |
Clear | Other pKa: 5.636. |
| 4.756 | +0.0002 -0.41 |
mM oC pKa |
Acetic acid HL = H+ + L-1 |
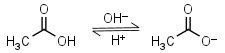 |
Clear | Volatile. |
| 5.03 (at 20oC) | mM 20oC pKa |
Pivalic (trimethylacetic) acid HL = H+ + L-1 |
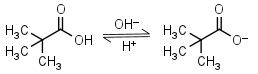 |
Clear | Volatile, has bad odor and relatively low solubility in water. | |
| 5.11 | mM 25oC pKa |
Malic acid HL-1 = H+ + L-2 |
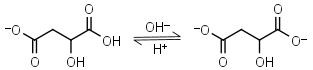 |
Clear | Other pKa: 3.40. Is chiral. Forms complexes with some metals. | |
| 5.39 (at 20oC) | mM 20oC pKa |
Picolinic acid HL± = H+ + L-1 |
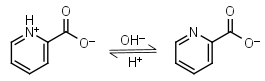 |
Other pKa: 0.99 at 20oC. | ||
| 5.636 | +0.0002 -0.5 |
mM oC pKa |
Succinic acid HL-1 = H+ + L-2 |
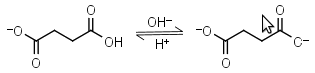 |
Clear | Other pKa: 4.207. |
| 6.14 | -0.0087 14.8 |
mM oC pKa |
MES HL± = H+ + L-1 |
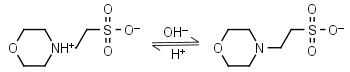 |
Clear | Other pKa: <3. Weekly binds Ca, Mg, Mn. Negligible binding with Cu(II).1,2 |
| 6.844 | -0.0072 12.23 |
mM oC pKa |
ADA HL-1 = H+ + L-2 |
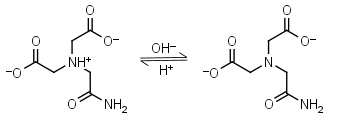 |
Opaque below 260 nm. | Other pKa: 1.59, 2.48. Binds Cu(II), Co(II), Zn(II), Mn(II), Ni(II), Ca(II), weakly binds Mg(II).3,4 |
| 6.847 | -0.018 30.43 |
mM oC pKa |
ACES HL± = H+ + L-1 |
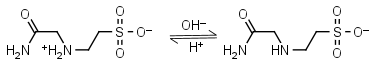 |
Opaque at 230 nm. | Other pKa: <3. Binds Cu(II), Co(II), Zn(II), Nil(II), week binding to Ca(II), Mg(II), negligible binding to Mn(II).1,5 |
| 6.90 | -0.015 25.0 |
mM oC pKa |
MOPSO HL± = H+ + L-1 |
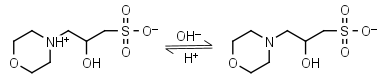 |
Clear | Other pKa: <2. Chiral, some metal binding. |
| 6.960 | -0.0072 12.3 |
mM oC pKa |
PIPES (HL±)-1 = H+ + L-2 |
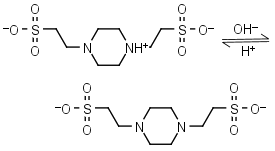 |
Clear | Other pKa: <3. Negligible binding to metals.1,2 Can form radicals, should be avoided in studies of oxidative compounds and redox processes in biochemistry.6,7 |
| 7.184 | -0.012 21.1 |
mM oC pKa |
MOPS HL± = H+ + L-1 |
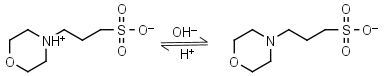 |
Clear | Other pKa: <2. Negligible binding to metals.2 Partially degrades on autoclaving in the presence of glucose. |
| 7.187 | -0.014 24.25 |
mM oC pKa |
BES HL± = H+ + L-1 |
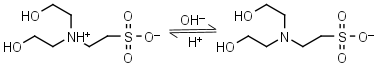 |
Clear | Other pKa: <3. Binds Cu(II), negligible binding to Ca(II), Mg(II) and Mn(II).1 |
| 7.198 | -0.0022 3.6 |
mM oC pKa |
Phosphoric acid H2L-1 = H+ + HL-2 |
H2PO4-1 = H+ + HPO4-2 | Clear | Other pKa: 2.148, 12.35. Stabilizes many enzymes. Precipitates bivalent cations. |
| 7.50 | -0.019 32.13 |
mM oC pKa |
TES HL± = H+ + L-1 |
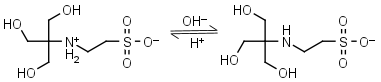 |
Clear | Other pKa: <3. Binds Cu(II), Co(II), Zn(II), Mn(II). Negligible binding to Ca(II), Mg(II) and Mn(II).1,8 |
| 7.564 | -0.012 20.4 |
mM oC pKa |
HEPES HL± = H+ + L-1 |
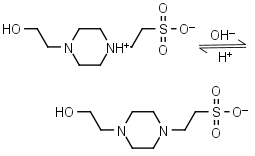 |
Clear | Other pKa: <3. Negligible binding to Ca(II), Mg(II) and Mn(II).1 Is oxidized by Cu(II).9 Can form radicals, should be avoided in studies of redox processes in biochemistry.6,7 |
| 7.576 | -0.018 30.18 |
mM oC pKa |
DIPSO HL± = H+ + L-1 |
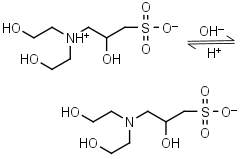 |
Clear | Other pKa: <2. Chiral. Binds Co(II), Ni(II).10 |
| 7.635 | -0.023 39.09 |
mM oC pKa |
TAPSO HL± = H+ + L-1 |
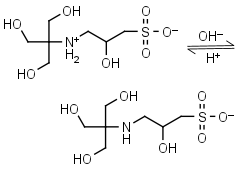 |
Clear | Other pKa: <2. Chiral. Binds Co(II), Ni(II).10 |
| 7.85 | -0.013 |
mM oC pKa |
POPSO (HL±)-1 = H+ + L-2 |
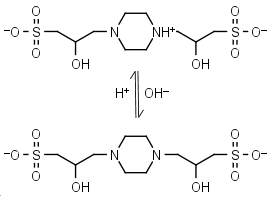 |
Clear | Other pKa: <2. Chiral, is a mixture of two diastereomers. Can form radicals, should be avoided in studies of redox processes in biochemistry.6,7 |
| 7.957 | -0.013 21.3 |
mM oC pKa |
EPPS, HEPPS HL± = H+ + L-1 |
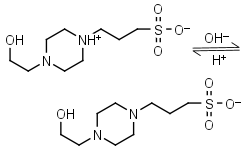 |
Clear | Other pKa: <2. Binds metals. Can form radicals, should be avoided in studies of redox processes in biochemistry.6,7 |
| 7.94 | -0.014 23.70 |
mM oC pKa |
HEPPSO HL± = H+ + L-1 |
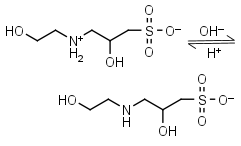 |
Clear | Other pKa: <2. Chiral. |
| 8.135 | -0.018 31.37 |
mM oC pKa |
Tricine HL± = H+ + L-1 |
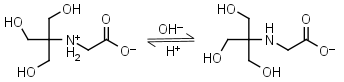 |
Clear | Other pKa: 2.023. Binds Cu(II), Co(II), Zn(II), Ni(II), Cd(II), Pb(II) Ca(II), Mg(II) and Mn(II).1,4 Is photooxidized by flavines. |
| 8.265 | -0.026 43.40 |
mM oC pKa |
Glycylglycine HL± = H+ + L-1 |
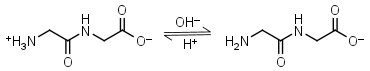 |
Clear | Other pKa: 3.14. Binds Cu(II) Mn(II), weakly binds Ca(II) and Mg(II).1 Is a primary amine, therefore it can form Schiff’s bases with aldehydes/ ketones. |
| 8.334 | -0.016 26.34 |
mM oC pKa |
Bicine HL± = H+ + L-1 |
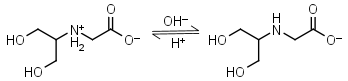 |
Clear | Other pKa: 2.0. Binds Cu(II), Co(II), Zn(II), Mn(II), Ca(II), Mg(II).1,8 Is slowly oxidized by ferricyanide. |
| 8.44 | -0.024 40.4 |
mM oC pKa |
TAPS HL± = H+ + L-1 |
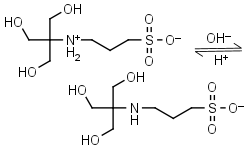 |
Clear | Other pKa: <2. Binds Co(II), Ni(II).10 |
| 9.138 | -0.025 43.19 |
mM oC pKa |
AMPSO HL± = H+ + L-1 |
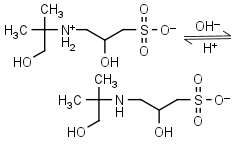 |
Clear | Other pKa: <2. Binds Co(II), Ni(II).10 Is chiral. |
| 9.237 | -0.008 13.8 |
mM oC pKa |
Boric acid HL = H+ + L-1 |
H3BO3 = H+ + H2BO3-1 | Clear | Forms covalent complexes with mono- and oligosaccharides, ribose subunits of nucleic acids, pyridine nucleotides. |
| 9.43 | -0.023 39.55 |
mM oC pKa |
CHES HL± = H+ + L-1 |
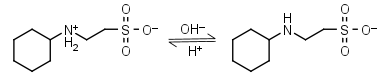 |
Clear | Other pKa: <3. |
| 9.780 | -0.026 44.2 |
mM oC pKa |
Glycine HL± = H+ + L-1 |
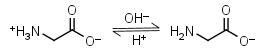 |
Clear | Other pKa: 2.351. Interferes with Bradford protein assay. Is a primary amine, therefore it can form Schiff’s bases with aldehydes/ ketones. |
| 9.825 | -0.027 46.67 |
mM oC pKa |
CAPSO HL± = H+ + L-1 |
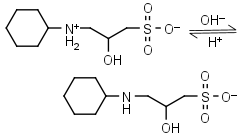 |
Clear | Other pKa: <2. Is chiral. |
| 10.499 | -0.028 48.1 |
mM oC pKa |
CAPS HL± = H+ + L-1 |
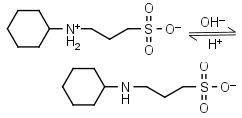 |
Clear | Other pKa: <2. |
| 10.7 | mM 25oC pKa |
CABS HL± = H+ + L-1 |
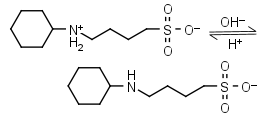 |
Clear | Other pKa: <2. |
*
Significant deviations exist in the reported values of pKa and other thermodynamic constants of most common buffers due to them being determined by methods of different accuracy. Additionally, many online resources provide pKa values of biological buffers at unspecified or wrongly specified ionic strengths. We attempted to provide the most consistent data available. pKa0, d(pKa)/dt and ΔH0 are compiled mostly from
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry & Physics, 93th edition: Dissociation Constants of Organic Acids and Bases.
- Goldberg, R. N., Kishore, N., Lennen, R. M. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 31, 2002, 231-370, as well as some other original publications.
If you have have experimentally observed significantly different values, please report them to support@reachdevices.com.
**Temperature dependence of pKa is presumed to be linear.
The best buffers for cation-exchange (white background):
- for concentrations 1 to 200mM, the Debye-Hückel model is used, and the resulting pKa is presented in brown font.
- for concentrations 201 to 500mM, the Davies model is used, and the resulting pKa is presented in blue font.
Less suitable buffers for cation-exchange (light brown background):
- for concentrations 1 to 50mM, the Debye-Hückel model is used, and the resulting pKa is presented in brown font.
- for concentrations 51 to 130mM, the Davies model is used, and the resulting pKa is presented in blue font.
For a detailed explanation of pKa vs pKa0, and formulas used in the calculator, click on this link.
The buffer is transparent at 200-700 nm range.
1 - Good, N. E., Winget, G. D., Winter, W., Connolly, T. N., Izawa, S., Singh. R. M. M. Biochemistry, 1966, 5, 467-477.
2 - Kandegedara, A., Rorabacher, D. B. Anal. Chem., 1999, 71, 3140-3144.
3 - Lance, E. A., Rhodes, C.W. , Nakon, R. Anal. Biochem., 1983, 133, 492-501.
4 - Nakon, R. Anal. Biochem., 1979, 95, 527-532.
5 - Pope, J. M., Stevens, P. R., Angotti, M. T., Nakon. R. Anal. Biochem., 1980, 103, 214-221.
6 - Grady, J. K., Chasteen, N. D., Harris. D. C., Anal. Biochem., 1988, 173, 111-115.
7 - Kirsch, M., Lomonosova, E. E., Korth, H.-G., Sustmann, R. de Groot, H. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1998, 273, 12716-12724.
8 - Nakon, R., Krishnamoorthy. C. R. Science, 1983, 221, 749-750.
9 - Hegetschweiler, K., Saltman, P. Inorg. Chem., 1986, 25, 107-109.
10 - Machado, C. M. M., Gameiro, P., Soares, H. M. V. M. J. Solution Chem., 2008, 37, 603-617.
REACH Devices, LLC.
6525 Gunpark Drive, Suite 370-179, Boulder, CO 80301
Call: (720) 288-5722
Inquiries: support@reachdevices.com
Ⓒ 2010-2025 REACH Devices, LLC. All rights reserved.